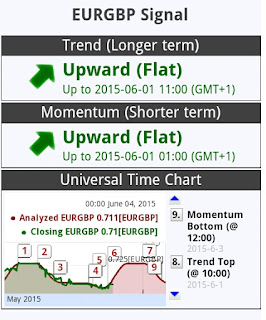
EURGBP stays around the lowest level for last 2 weeks. While Greek officials are optimistic about their deal approved, other European countries require reforms in Greek economy, including pension scheme and privaterization in public sectors.
From the point of technical analysis, the trend and momentum indicates EURGBP is expected higher for a coming week. European countries and Greece aim to agree the deal by the end of May, andaagreement will mitigate EUR risk, EUR going up.
FOREX FLYER is a source of analysis tips for forex, investment and trading. Official blog of QROSS X and Newsensus.
Translate to your language:)
Friday, 29 May 2015
Friday, 22 May 2015
EURUSD trend & momentum 22-May-2015
EURUSD has steeply fallen for a week , and it currently stays around 1.102 . Greek deal still has to be observed cafrefully as the situation can change daily basis.
The trend and momentum of EURUSD indicates it is gradually recovered in upward trend.
In addition to Greek deal, US economic situation drive the expectation of interest rate.
The trend and momentum of EURUSD indicates it is gradually recovered in upward trend.
In addition to Greek deal, US economic situation drive the expectation of interest rate.
Wednesday, 20 May 2015
Currency is stronger when the economy growing
On the other hand, particularly Japanese economy, it has been said strong currency prevent the recovery and weak JPY is better for the economy. Weak currency may help exporters to rise revenues in their local currency while importers suffer from cost rising in the local currency.
Weak currency could lead to excessive inflation. In order to control inflation, long term interest rate have to be pushed up. However, it implies the lending cost become more expensive and their credit is degraded.
In terms of credit, strong currency is generally good for the economy. But why some government prefer their currencies weaker? One fact is that weak currency makes their debt smaller. In economic zones where "borrowed" exceeds "borrowing", lower currency helps their debt be shrink.
Even if strong currency convinces healthy credit, it is still unclear that the economy is actually recovered and financially sustainable. Below tables shows economic indicators for US, UK, Japan and Australia.
 |
| (Blue indicates maximum number and Red indicates minimum.) |
Long rate bench mark: 10 year government bond yield.
(Debt / GDP)
The figure of Japan is 227.20%, which means government debt is more than twice of GDP. This figure is outstanding in developed countries. Even Greece currently struggling with their financial situation, the figure is 177.10%. According to Debt/ GDP, Japan is facing financially difficult situation though they have great industries such as auto industry.
On the other hand, Australian figure is 28.60% which is one of the lowest levels of developed countries. However, Australian interest rates have sharply fallen for the last few years, and the economy is not growing as well as before because mining industry had been shrink. Australian government could borrow more due to such economic situation, helped by the lowered interest rate.
(Inflation, Interest rate and FX)
Looking at Inflation y/y and interest rate target, Japanese figure only indicates the inflation is higher than short rate target and long rate bench mark. One reason of this figure is that increased consumer tax has driven the inflation. However, as the inflation is lower than interest rate benchmark, monetary policy is still eased to provide money into the market. The central bank should seek timing to tighten the policy in order to control inflation.
On the other hand, US and UK figures indicate they are facing deflation, despite the record low interest rate. Since later 2014, crude oil price has fallen and it helped consumer price down. Their strong currencies also helped the price of import goods down, too. Both factors are good for them, and the deflation is unlikely considered as weak production.
Ref)
Trading economics
World Interest Rates - FX street
Investing.com
Check international business news on Newsensus. Available on GooglePlay
Tuesday, 12 May 2015
NZD expected under jumping risk toward RBNZ financial stability report
NZD has been relatively weaken against major currencies, particularly GBP or USD since beginning of 2015.
RBNZ has been expected to cut interest rate since early this year. See a related post.
NZD is weak towards RBNZ releasing financial stability report in today's evening GMT. It implies the market consensus still expect downside at interest rate. Even US and UK are still hesitating to rise interest rate, and RBNZ is unlikely to change their stance to the policy.
Ref (picked up on Newsensus ) NZ dollar falls ahead of RBNZ report, retail sales
GBPNZD trend & momentum chart
Check international business news on Newsensus. Available on GooglePlay
RBNZ has been expected to cut interest rate since early this year. See a related post.
NZD is weak towards RBNZ releasing financial stability report in today's evening GMT. It implies the market consensus still expect downside at interest rate. Even US and UK are still hesitating to rise interest rate, and RBNZ is unlikely to change their stance to the policy.
Ref (picked up on Newsensus ) NZ dollar falls ahead of RBNZ report, retail sales
GBPNZD trend & momentum chart
Check international business news on Newsensus. Available on GooglePlay
Labels:
Economy,
GBP,
GBPNZD,
Long term,
News,
NZD,
NZDUSD,
Short term,
Trend & Momentum
Monday, 11 May 2015
Stock market driven by interest rate, financial aid is harder in ending than starting
Since central banks in the world have been rushing to cut their interest rates and bring quantitative easing, the trend in such as stock markets is being driven by monetary policy.
In typical scenario, the stock market soars after the interest rate has been cut or quantitative easing has been taken. While this is under the recovery process, counter effect is likely to be caused in the ending process. The counter effect implies stock market vulnerable to rate hike or quantitative easing finished.
In fact, we have seen some examples of the counter effect in US. The market sometimes reacts negatively when released economic indicators are too good as outstanding recovery is thought to lead interest rate hike and current liquidity can be degraded.
Pick up from CNBC >>
"Good news is bad news again," said Gina Martin Adams at Wells Fargo. Adams said there was a quick jump in the Fed Funds futures this morning. "The percentage chance for a June hike went from 18 percent to 25 percent," she said.
February's nonfarm jobs report showed a gain of 295,000, above expectations of 240,000 in February, down from 257,000 in January. The unemployment rate fell to 5.5 percent, while hourly wages ticked up 0.1 percent, below consensus and off the surprise 0.5 percent gain in January.
Today, Bank of England kept the interest rate unchanged at 0.50%. UK economy has recovered, following to US economy. The market is paying attention to when the interest rate is going up and the ending process of financial aid is likely as tough as US.
Ref.
CNBC - US stocks fall sharply on fears of pending rate hikes; Dow below 18K
FT - Bank of England keeps rates and monetary policy on hold
Check international business news on Newsensus. Available on GooglePlay
In typical scenario, the stock market soars after the interest rate has been cut or quantitative easing has been taken. While this is under the recovery process, counter effect is likely to be caused in the ending process. The counter effect implies stock market vulnerable to rate hike or quantitative easing finished.
In fact, we have seen some examples of the counter effect in US. The market sometimes reacts negatively when released economic indicators are too good as outstanding recovery is thought to lead interest rate hike and current liquidity can be degraded.
Pick up from CNBC >>
"Good news is bad news again," said Gina Martin Adams at Wells Fargo. Adams said there was a quick jump in the Fed Funds futures this morning. "The percentage chance for a June hike went from 18 percent to 25 percent," she said.
February's nonfarm jobs report showed a gain of 295,000, above expectations of 240,000 in February, down from 257,000 in January. The unemployment rate fell to 5.5 percent, while hourly wages ticked up 0.1 percent, below consensus and off the surprise 0.5 percent gain in January.
Today, Bank of England kept the interest rate unchanged at 0.50%. UK economy has recovered, following to US economy. The market is paying attention to when the interest rate is going up and the ending process of financial aid is likely as tough as US.
Ref.
CNBC - US stocks fall sharply on fears of pending rate hikes; Dow below 18K
FT - Bank of England keeps rates and monetary policy on hold
Check international business news on Newsensus. Available on GooglePlay
Monday, 4 May 2015
[Interest rate] Forward rate of LIBOR
Interest rate mentioned in this post means short rate such as LIBOR or EURIBOR. Forward rate is the expected interest rate in future, derived from financial market. The forward rate in USD typically going up along with tenor.
The question is how the forward rate is reliable while the interest rate has always stayed low for a last several years despite forward rate expected higher level all the time.
Ultimately and generally, no one knows interest rate in the future, but mathematical model has challenged to predict the trend of interest rate in stochastic differential formulae which non-mathematician do not have to know details as it may annoy you.
Even though the mathematical methodology is hard for the most of people to understand, it is important to know two approaches to predict the future rate in the modelling. One estimates the parameters by observing financial instruments in the market, which can be interest rate swap. Another estimates the parameters from historical data of the interest rate.
When bankers or traders talk about forward rate, it typically implies the first approach which estimates higher rate. On the other hand, despite the gap between the forward rate and reality, people has not mentioned about the forward rate derived from the historical data, so now time to see how different between those two approaches in the forward rate.
 The chart describes historical USD 3M LIBOR in last 10 years, the forward rate derived from historical data in last 30 years and the forward rate derived from current financial market.
The chart describes historical USD 3M LIBOR in last 10 years, the forward rate derived from historical data in last 30 years and the forward rate derived from current financial market.
The point is the huge gap between the two different forward curves. As the lowest rate in a last few years, the market consensus seems to expect the lower rate in the future. However, the market still expect relatively higher interest rate compared with the rate estimated from historical data. Historical period covers the period when the interest rate had been certainly high level.
Forward rate by market has been always shape like that in the figure, but the rate has stayed low. The forward rate will betray again or it is actually time interest rate going up?
The question is how the forward rate is reliable while the interest rate has always stayed low for a last several years despite forward rate expected higher level all the time.
Ultimately and generally, no one knows interest rate in the future, but mathematical model has challenged to predict the trend of interest rate in stochastic differential formulae which non-mathematician do not have to know details as it may annoy you.
Even though the mathematical methodology is hard for the most of people to understand, it is important to know two approaches to predict the future rate in the modelling. One estimates the parameters by observing financial instruments in the market, which can be interest rate swap. Another estimates the parameters from historical data of the interest rate.
When bankers or traders talk about forward rate, it typically implies the first approach which estimates higher rate. On the other hand, despite the gap between the forward rate and reality, people has not mentioned about the forward rate derived from the historical data, so now time to see how different between those two approaches in the forward rate.
 The chart describes historical USD 3M LIBOR in last 10 years, the forward rate derived from historical data in last 30 years and the forward rate derived from current financial market.
The chart describes historical USD 3M LIBOR in last 10 years, the forward rate derived from historical data in last 30 years and the forward rate derived from current financial market. The point is the huge gap between the two different forward curves. As the lowest rate in a last few years, the market consensus seems to expect the lower rate in the future. However, the market still expect relatively higher interest rate compared with the rate estimated from historical data. Historical period covers the period when the interest rate had been certainly high level.
Forward rate by market has been always shape like that in the figure, but the rate has stayed low. The forward rate will betray again or it is actually time interest rate going up?
Saturday, 2 May 2015
[App] Newsensus quick tutorial 2-May-2015
Android app, Newsensus, reads and displays world news on your mobile, based on consensus flowed in the media.
This is a quick tutorial how to use Newsensus though the app itself is simple and easy to use.
1) Tap an economic zone you're interested.
2) Choose a subject in the economic zone.
3) You will find more details of the story once you tap on the headline.
Newsensus is aimed at assisting international business people by facilitating to find business, financial and economic news in the world. You will be able to check regional business news globally in a single platform, which allows to turn from an economic zone to another.
We consider consensus as one of the key measures to understand what people are interested, and understanding the consensus could help business people to grab chances.
Available on Google Play.
This is a quick tutorial how to use Newsensus though the app itself is simple and easy to use.
1) Tap an economic zone you're interested.
2) Choose a subject in the economic zone.
3) You will find more details of the story once you tap on the headline.
Newsensus is aimed at assisting international business people by facilitating to find business, financial and economic news in the world. You will be able to check regional business news globally in a single platform, which allows to turn from an economic zone to another.
We consider consensus as one of the key measures to understand what people are interested, and understanding the consensus could help business people to grab chances.
Available on Google Play.
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)